| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- 그로스 해킹
- pmdarima
- WITH CUBE
- 캐글 신용카드 사기 검출
- splitlines
- 부트 스트래핑
- sql
- 스태킹 앙상블
- 인프런
- 캐글 산탄데르 고객 만족 예측
- 3기가 마지막이라니..!
- ImageDateGenerator
- 로그 변환
- 그룹 연산
- 마케팅 보다는 취준 강연 같다(?)
- tableau
- 리프 중심 트리 분할
- WITH ROLLUP
- DENSE_RANK()
- ARIMA
- 데이터 핸들링
- python
- 분석 패널
- 데이터 정합성
- 컨브넷
- lightgbm
- Growth hacking
- 데이터 증식
- 그로스 마케팅
- XGBoost
- Today
- Total
LITTLE BY LITTLE
[1] 캐글 RSNA 2022 Cervical Spine Fracture Detection 본문
RSNA 2022 Cervical Spine Fracture Detection
https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/rsna-2022-cervical-spine-fracture-detection/overview/evaluation
RSNA 2022 Cervical Spine Fracture Detection | Kaggle
www.kaggle.com
- 목표
- To Develop Machine Learning Models that match the radiologists' performance in Detecting and Localizing features to the 7 vertebrae that comprise the cervical spine.
- 척추 골절 중 가장 흔한 경추(cervical spine)에 대해 다룸
- 특히 노인들 사이 척추 골절이 많이 발생하고 있는데, 골절은 퇴행성 질환과 골다공증 때문에 발견하는 것이 어려움
- 골절 진단시 x-rays (radiographs)가 아닌 CT (computed tomography)로 이루어지고 있음
- 트라우마 이후 neaurologic deterioration(coma와 유사한 증상) 과 마비를 방지하기 위해서 척추 골절의 위치를 파악하는 것이 중요함
- 평가 방법
- weighted multi-label logarithmic loss
- 예측해야하는 것들은
- a prob for a fracture at each of the 7 cervical vertebrae ( C1~C7 )
- fractures' sub type is its own row for every exam
- overall prob of any fractures in the cervical spine
- 이를 예측하기 위한 any label이 존재 'patient_overall' : indicates that fracture of ANY kind described before exists in the examination. Fractures in the skull base, thoracic spine, ribs, and clavicles are ignored. => The any label is weighted more highly than specific fracture level sub-types( C1~C7 ).)
- a prob for a fracture at each of the 7 cervical vertebrae ( C1~C7 )
- must submit a set of predicted probabilities (a separate row for each cervical level subtype). We then take the log loss for each predicted probability versus its true label.

선행 연구
CNN을 사용한 경추 골절 detection에 대한 평가
: Results part
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8324280/
CT Cervical Spine Fracture Detection Using a Convolutional Neural Network
Multidetector CT has emerged as the standard of care imaging technique to evaluate cervical spine trauma. Our aim was to evaluate the performance of a convolutional neural network in the detection of cervical spine fractures on CT.We evaluated C-spine, ...
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Abstract
Aim :
x-ray와의 비교를 통한 경추 골절 CT에 쓰이는 CNN의 성능 평가
to evaluate the performance of a convolutional neural network (CNN) developed by Aidoc (www.aidoc.com) for the detection of cervical spine fractures on CT.
- CNN 성능을 X-ray 성능과 비교 We establish the presence of fractures based on retrospective clinical diagnosis and compare the CNN performance with that of radiologists.
- Aidoc’s CNN currently runs continuously on our hospital system and functions as a triage and notification software for analysis and detection of cervical spine fractures.
- However, we purposefully conducted a retrospective study on cervical spine studies performed before system-wide deployment, as we wanted to compare CNN performance to radiologist performance without the aid of the tool. A proficient algorithm may help identify and triage(중증도 분류) studies for the radiologist to review more urgently, helping to ensure faster diagnoses.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
- We evaluated C-spine, an FDA-approved convolutional neural network developed by Aidoc to detect cervical spine fractures on CT.
- 665 examinations are included.
- The ĸ coefficients, sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values were calculated with 95% CIs
RESULTS:
- Convolutional neural network accuracy in cervical spine fracture detection was 92% (95% CI, 90%–94%), with 76% sensitivity and 97% specificity.
- The radiologist accuracy was 95% (95% CI, 94%–97%), with 93% sensitivity and 96% specificity.
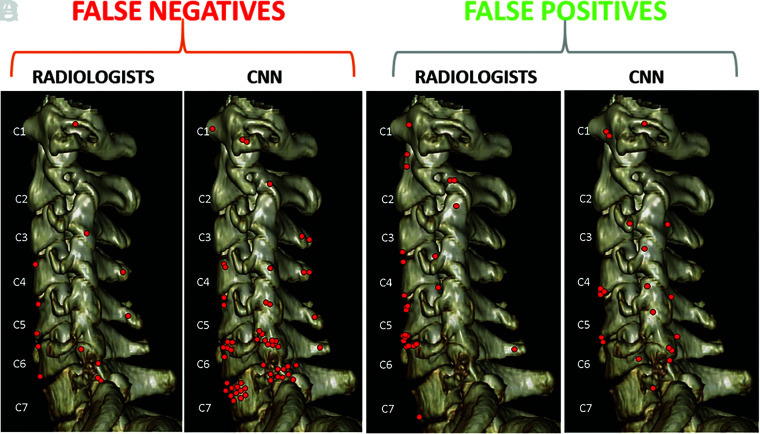
- Fractures missed by the convolutional neural network and by radiologists were similar by level and location and included fractured anterior osteophytes, transverse processes, and spinous processes, as well as lower cervical spine fractures that are often obscured by CT beam attenuation.
CONCLUSIONS:
- The convolutional neural network holds promise at both worklist prioritization and assisting radiologists in cervical spine fracture detection on CT.
- Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the convolutional neural network is essential before its successful incorporation into clinical practice.
- Further refinements in sensitivity will improve convolutional neural network diagnostic utility.
- 선행 연구가 많이 없음 (필요성 제시1)
- To our knowledge, no studies evaluating AI in detecting cervical spine fractures on CT have been published.
- 경추 골절 많이 일어남 (필요성 제시2)
- Cervical spine injury is common with greater than 3 million patients per year being evaluated for cervical spine injury in North America, and greater than 1 million patients with blunt trauma with suspected cervical spine injury per year being evaluated in the United States.
- 경추 골절 발견의 필요성 (필요성 제시3)
- Cervical spine injury can be associated with high morbidity and mortality,and a delay in diagnosis of an unstable fracture leading to inadequate immobilization may result in a catastrophic decline in neurologic function with devastating consequences.
- Clearing the cervical spine through imaging is therefore a critical first step in the evaluation of patients with trauma, and multidetector CT has emerged as the standard of care imaging technique to evaluate cervical spine trauma.
- Morbidity and mortality in patients with cervical spine injury can be reduced through rapid diagnosis and intervention.
Part 1
- 869개의 경추 CT 진찰이 가장 먼저 발견됨
- 환자들의 나이는 16세-98세, 평균 60.28세, 중위값은 61세
- 전체 환자 중 54.5%(379명)는 남자, 45.5%(316명)는 여자
- 12개의 데이터가 duplicates
- Excluded datasets
- 162개의 진찰이 CNN을 통과하지 못하였다.
- 그리고 162개 중 157개는 PACS(의료영상저장전송시스템)으로부터 가져오지 못함
- 그 이유는 idenfiable DICOM header 이 없는 외부 병원으로부터 수집되었기 때문
- 나머지 5개는 CNN으로 분석할 수 없었다. (because of the technical issues with the datasets)
- 여기서의 technical issues는 CNN orchestrator의 전처리 과정과 관련이 있다.
- 여기에는 일정하지 않은 DICOM tags와 missing slices 등이 포함됨
- 제외된 데이터와 포함된 데이터 모두 fracture prevalance는 유사하였다.
- 예를 들면, 제외된 데이터162 개 중 35개는 양성(22%) 이었고, 포함된 데이터 695개 중 143개는 양성(21%)으로, 양성인 정도가 유사함
- 위는 CNN을 실행시키기 이전에 얻은 데이터이기 때문에, CNN을 실행시킨 후 얻은 데이터 중 제외된 데이터의 비율은 더 적다.
- availability of technical support from the CNN Developer and the presence of reliable DICOM tags 덕분
- 결과적으로, CNN의 정확도는 본 연구에서의 정확도와 비교할만하다고 판단됨
- 포함된 695개의 남아있는 데이터 중 30개는 경추(C1-C7)가 아닌 외부 골절을 포함하고 있었기 때문에, 본 연구에서 제외되었다.
- 따라서 최종 샘플 사이즈는 665개
- 그 중 143개가 양성, 522개가 음성으로 labeled
Part 2 : x-ray 성능 result (radioogists) / CNN 성능 result
- true-positive(골절이 있다고 언급되고, 실제로도 양성) : 133개 / 109개
- true-negative(골절이 없다고 언급되고, 실제로도 음성) : 502개 / 505개
- false-positive(골절이 있다고 언급되었으나, MR imaging과 CNN 결과상에서는 음성) : 20개 / 17개
- false-negative(골절이 없다고 언급되었으나, MR imaging과 CNN 결과상에서는 양성 & could be visualized in retrospect on the cervical spine CT) : 10개 / 34개
- 따라서 PPV = 87% (95%CI 81-92%) / 동일
- NPV = 98% (CI 97%-99%) / 94% (CI 91%-96%)
- Sensitivity = 93% (CI, 88-97%) / 76% (CI 58%-83%)
- Specificity - 96% (CI, 94-98%) / 97% (CI 95%-98%)
- Percent Agreement = 95.5% (CI, 94-97%) / 92% (CI 90%-95%)
- ĸ coefficient = 0.87 (CI, 0.82-0.92) / 0.76 (CI 0.70-0.82)
- 걸린 시간 The time from acquisition until a finalized report for the radiologist ranged from 33-43 min / 3-8 min
Part 3 :
- radiologist가 놓친 true-positive 중 7개는 CNN이 발견하였다.
- CNN이 발견한 true-positive 중 4개는 chronic